Perfusion Weighted Imaging (PWI)
Physiological brain imaging, known as perfusion imaging, involves a combination of structural and physiological imaging techniques performed using an MRI machine with a strength of either 1.5T or 3T. Initially, raw and primary images are acquired using perfusion protocols based on T1 for calculating DCE (Dynamic Contrast Enhanced) or based on T2 for calculating DSC (Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast). These calculations are performed by the imaging device, which is equipped with the necessary protocols, processing capabilities, and calculation algorithms. If further analysis and quantitative calculations are required, the images and signals are transferred to high-performance computers equipped with specialized software for spectrum information analysis and quantification. The obtained information is then qualitatively corrected, measured, and statistically validated. Various perfusion maps are generated and overlaid on standard anatomical images, which are subsequently printed in color. Perfusion images and maps, depicting the lesion sites, surrounding areas, and corresponding healthy tissue, are utilized for differential diagnoses that cannot be achieved through conventional MRI imaging techniques (Dynamic Contrast Enhanced) .
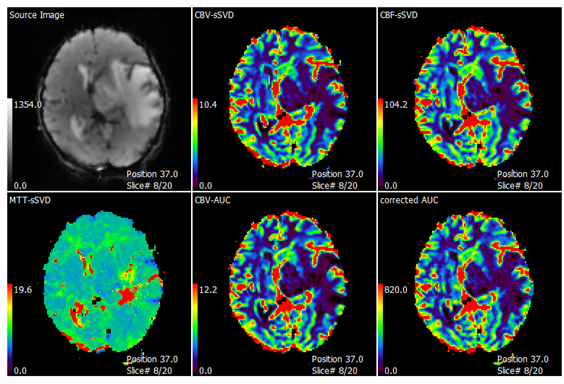
Perfusion maps displaying various parameters are derived from the analysis of DSC images. (These maps provide valuable information about blood flow and related physiological parameters in the brain).
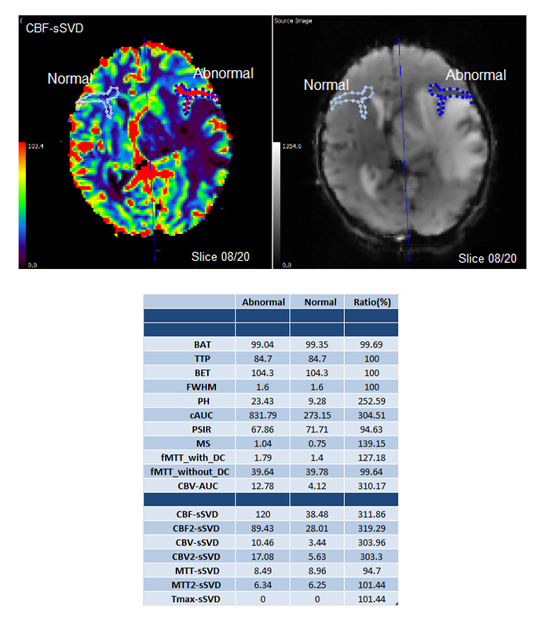
.
